In today’s hyper-connected world, where digital transformation is no longer an option but a strategic imperative, organizations face an increasingly complex tapestry of cyber threats and operational vulnerabilities. The sheer volume and sophistication of these risks demand a structured approach to safeguard critical assets and ensure business continuity. Today, let’s join Daily98news to find out why a robust information technology risk management framework is not merely a compliance checklist but a fundamental pillar for sustainable growth and competitive advantage in the digital age. This article will delve into the core tenets, practical applications, and evolving landscape of managing IT risks, providing clarity amidst the buzzwords.
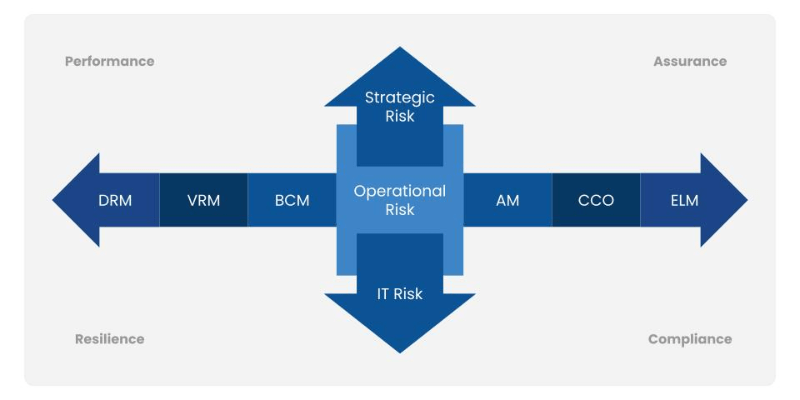
Understanding the critical role of an information technology risk management framework
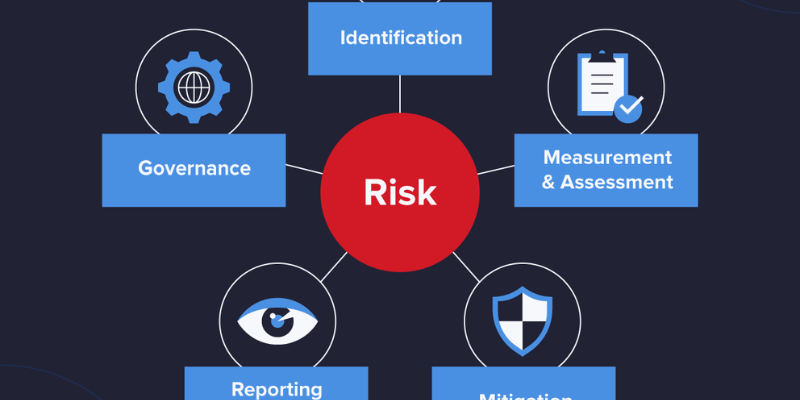
The digital landscape is constantly shifting, introducing novel challenges alongside opportunities. An information technology risk management framework provides a structured methodology for identifying, assessing, mitigating, and monitoring these risks across an organization’s IT ecosystem. It transforms an ad-hoc response into a proactive, strategic function, aligning IT security with broader business objectives. This framework acts as a compass, guiding decision-makers through the intricate terrain of digital hazards and ensuring that technology investments are protected and yield their intended value.
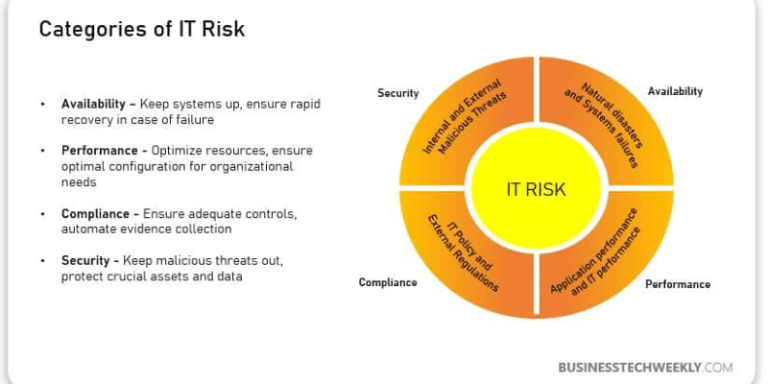
What constitutes IT risk?
IT risk encompasses any potential threat that could negatively impact an organization’s information systems, data, or technology infrastructure. These risks can originate.
Why a structured approach is essential
A structured approach to IT risk management moves beyond isolated security measures to integrate risk considerations into every aspect of an organization’s operations. It fosters a culture of security awareness, ensuring that employees at all levels understand their role in protecting digital assets. Such a framework enables organizations to prioritize risks based on their potential impact and likelihood, allocating resources efficiently to address the most critical vulnerabilities first. This systematic methodology also facilitates better communication between IT departments and executive leadership, translating technical risks into business language that supports informed decision-making. By providing a clear roadmap, it helps avoid knee-jerk reactions to incidents and instead promotes a resilient, adaptive posture.
Key components of a robust risk management framework
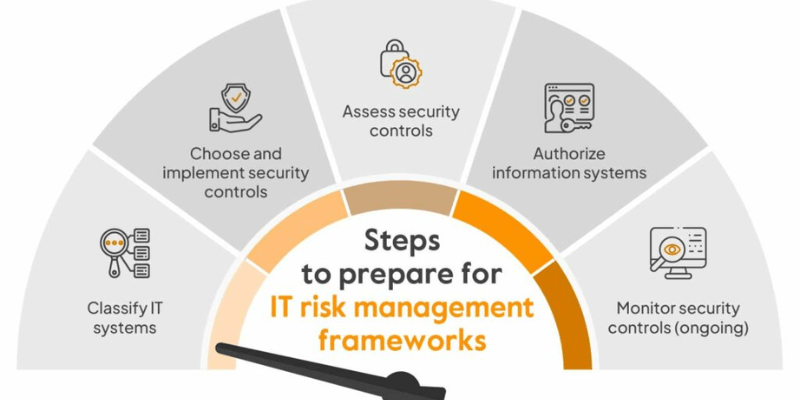
An effective information technology risk management framework is built upon several foundational components that work in concert to provide comprehensive coverage. These components guide organizations through the entire risk lifecycle,, businesses can establish a strong defense against the ever-evolving threat landscape.
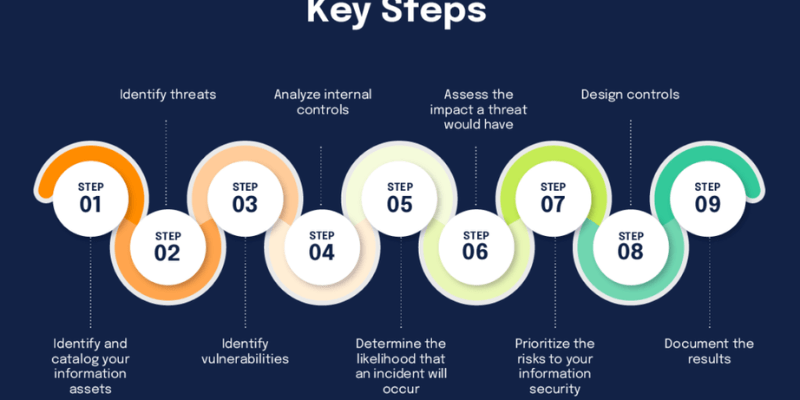
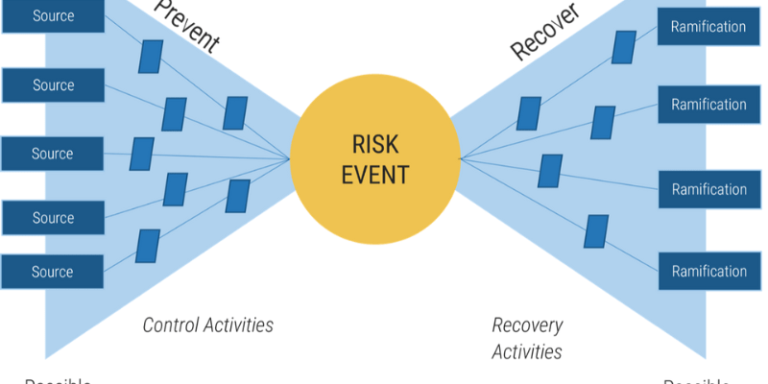
Risk identification and assessment
The initial phase involves meticulously identifying all potential IT risks within an organization’s environment. This includes reviewing hardware, software, network infrastructure, data processes, and human factors. Once identified, risks are assessed based on their likelihood of occurrence and their potential impact on business operations, financial standing, and reputation. This assessment often uses qualitative (e.g., high, medium, low) or quantitative (e.g., financial cost) methods to provide a clear understanding of the threat landscape. For example, assessing the likelihood of a data breach from a zero-day vulnerability might be high given the prevalence of such attacks, while the impact on customer trust and regulatory fines could be catastrophic. Tools like vulnerability scanners and penetration testing are crucial here.
Risk response and mitigation strategies
After risks are assessed, organizations must develop appropriate response and mitigation strategies. These strategies typically fall into four categories: avoidance, transference, acceptance, and mitigation. Avoidance involves eliminating the risk entirely, such as discontinuing a risky project. Transference shifts the risk to a third party, often through insurance. Acceptance means acknowledging the risk and deciding not to take any action, usually for low-impact, low-likelihood risks. Mitigation, the most common approach, involves implementing controls to reduce the likelihood or impact of the risk. This could include deploying firewalls, encrypting sensitive data, or implementing robust access controls. Each strategy requires careful consideration of cost, effectiveness, and alignment with business goals.
Continuous monitoring and review
The dynamic nature of technology and threats necessitates continuous monitoring and periodic review of the information technology risk management framework. This involves regularly scanning for new vulnerabilities, monitoring security events, and reviewing the effectiveness of existing controls. As new technologies are adopted or business processes change, new risks may emerge, requiring adjustments to the framework. Regular audits and assessments help identify gaps and ensure that the risk management process remains relevant and effective. Companies often use Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems to aggregate and analyze security logs, providing real-time insights into potential threats and compliance deviations. This ongoing vigilance is paramount for maintaining a strong security posture.
Implementing an effective information technology risk management framework
Implementing an effective information technology risk management framework is a complex undertaking that requires careful planning, executive buy-in, and a clear understanding of an organization’s specific context. It’s not a one-size-fits-all solution but rather a tailored process that aligns with the organization’s strategic objectives, regulatory requirements, and risk appetite. The success of implementation hinges on a phased approach, fostering collaboration across departments, and embedding risk awareness into the organizational culture. This strategic deployment ensures that the framework becomes an integral part of operations rather than an isolated security initiative.
Establishing governance and policies
The foundation of any successful risk management framework is strong governance. This involves establishing clear roles, responsibilities, and accountability for risk management activities across the organization. Senior leadership must champion the initiative, providing the necessary resources and demonstrating a commitment to security. Policies and procedures need to be developed that define acceptable use of technology, data handling protocols, incident response plans, and compliance requirements. These policies serve as the guiding principles for employees, ensuring a consistent approach to risk across all business units. Regular training and communication are essential to ensure that all stakeholders understand their obligations and the importance of these policies.
Integrating with business processes
For an information technology risk management framework to be truly effective, it cannot exist in a silo. It must be seamlessly integrated into existing business processes and workflows. This means considering risk implications during the planning stages of new projects, applications, and system deployments. Incorporating risk assessments into the software development lifecycle (SDLC) helps identify and address vulnerabilities early, reducing remediation costs later. Furthermore, integrating risk management with broader enterprise risk management (ERM) initiatives ensures a holistic view of risks across the entire organization, preventing IT risks.
Leveraging technology and automation
Modern IT risk management relies heavily on technology and automation to manage the sheer volume of data and rapidly evolving threats. Tools such as Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) platforms, vulnerability management systems, and security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR) solutions streamline processes, improve efficiency, and enhance accuracy. Automation can accelerate risk assessments, identify anomalies in real time, and even initiate predefined responses to security incidents. For instance, automated vulnerability scanning can continuously monitor systems for known weaknesses, while an automated incident response playbooks can guide security teams through critical steps during an attack, reducing human error and response times. These technological enablers are crucial for maintaining an up-to-date and dynamic risk posture.
Benefits and business impact of strong IT risk management
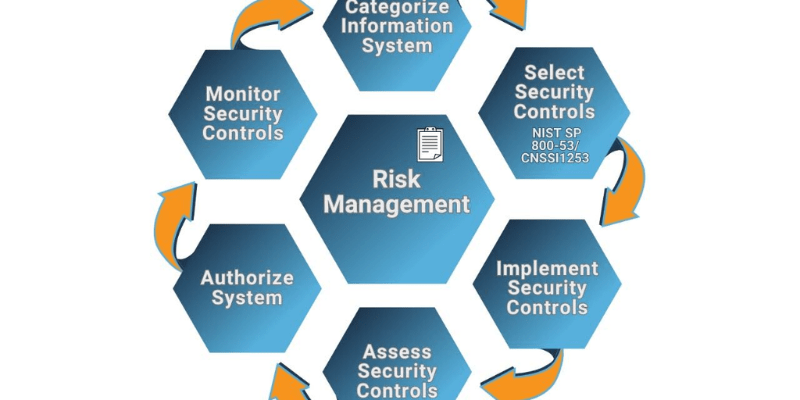
Implementing a robust information technology risk management framework extends far beyond simply avoiding breaches or ensuring compliance; it fundamentally enhances an organization’s operational resilience and strategic agility. The benefits permeate various aspects of the business, fostering greater trust among customers and stakeholders, optimizing resource allocation, and even serving as a competitive differentiator in the marketplace. Companies that proactively manage their IT risks are better positioned to navigate unforeseen challenges and capitalize on new technological opportunities, ultimately driving long-term value.
Enhanced security posture and resilience
A well-implemented framework significantly strengthens an organization’s overall security posture. By systematically identifying and addressing vulnerabilities, companies can reduce their attack surface and minimize the likelihood of successful cyberattacks. In the event of an incident, a prepared organization with a defined incident response plan, a core component of risk management, can react swiftly and effectively, limiting damage and accelerating recovery. This enhanced resilience means less downtime, reduced data loss, and quicker restoration of normal operations, all of which directly impact profitability and customer satisfaction. It transforms a reactive defense into a proactive, adaptive system.
Regulatory compliance and reputation protection
In an era of stringent data privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA, and industry-specific mandates, demonstrating compliance is non-negotiable. An information technology risk management framework provides the documented processes and controls necessary to meet these regulatory obligations, avoiding hefty fines and legal repercussions. Beyond compliance, protecting sensitive data and maintaining operational integrity safeguards an organization’s reputation. Data breaches can severely erode customer trust and public perception, leading to long-term damage to brand equity. A strong risk management framework acts as a shield, preserving the trust that customers and partners place in the organization.
Improved decision-making and resource allocation
By providing clear insights into the organization’s risk landscape, an IT risk management framework empowers leadership to make more informed strategic and operational decisions. Resources, whether financial or human, can be allocated more effectively to address the most critical risks, ensuring maximum impact.
Evolving threats and the future of IT risk management
The pace of technological innovation is matched only by the increasing sophistication of cyber threats. New paradigms like artificial intelligence, quantum computing, and the widespread adoption of IoT devices are introducing novel risk vectors that traditional frameworks may not fully address. Therefore, the future of information technology risk management framework must be adaptive, forward-looking, and continuously integrate emerging technologies and methodologies to stay ahead of adversaries. Daily98news recognizes that staying abreast of these shifts is critical for any organization aiming for long-term digital security.
AI and machine learning in risk management
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are rapidly transforming the field of IT risk management. These technologies can process vast amounts of data to identify patterns, detect anomalies, and predict potential threats with unprecedented speed and accuracy. AI-powered tools can enhance threat detection, automate vulnerability assessments, and even assist in forensic analysis after an incident. For example, AI algorithms can analyze network traffic to spot unusual behavior indicative of an attack before it fully escalates, offering predictive capabilities that human analysts might miss. However, AI also introduces new risks, such as algorithmic bias or adversarial AI attacks, which must be managed within the framework itself.
The challenge of quantum computing and IoT security
The advent of quantum computing poses a long-term, yet significant, threat to current encryption standards, which form the bedrock of much of modern cybersecurity. Organizations need to start considering “post-quantum cryptography” readiness as part of their future risk strategies. Simultaneously, the proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices,, making them easy targets for attackers seeking to gain entry into corporate networks or launch large-scale distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks. Managing the security and risk associated with these myriad, often resource-constrained devices, is a growing challenge that demands specialized attention within the IT risk management framework.
The rise of supply chain and third-party risks
Modern businesses increasingly rely on a complex web of third-party vendors, cloud providers, and supply chain partners. This extended ecosystem, while enabling agility and specialization, also introduces significant inherent risks. A vulnerability in a single supplier’s system can have a cascading effect, compromising the data and operations of numerous clients, as evidenced by recent high-profile supply chain attacks. Therefore, an information technology risk management framework must extend its purview beyond the organization’s immediate perimeter to include thorough vetting, continuous monitoring, and contractual agreements with all third parties. Robust due diligence and clear service level agreements regarding security are paramount to mitigate these pervasive external risks.
Conclusion
A well-defined and diligently executed information technology risk management framework is no longer a luxury but an indispensable strategic asset in the contemporary digital economy. It provides the necessary structure and foresight to navigate an increasingly complex threat landscape, safeguarding critical assets, ensuring regulatory compliance, and bolstering an organization’s overall resilience. Daily98news encourages all technology leaders and business owners to invest in developing and continuously refining their IT risk management strategies, transforming potential vulnerabilities into areas of strength. By embracing a proactive and adaptive approach, organizations can build trust, protect their reputation, and confidently leverage technology to achieve their strategic objectives in an ever-evolving digital world.# Navigating the Digital Frontier: An Information Technology Risk Management Framework Imperative
In today’s hyper-connected world, where digital transformation is no longer an option but a strategic imperative, organizations face an increasingly complex tapestry of cyber threats and operational vulnerabilities. The sheer volume and sophistication of these risks demand a structured approach to safeguard critical assets and ensure business continuity. Today, let’s join Daily98news to find out why a robust information technology risk management framework is not merely a compliance checklist but a fundamental pillar for sustainable growth and competitive advantage in the digital age. This article will delve into the core tenets, practical applications, and evolving landscape of managing IT risks, providing clarity amidst the buzzwords.
Understanding the critical role of an information technology risk management framework
The digital landscape is constantly shifting, introducing novel challenges alongside opportunities. An information technology risk management framework provides a structured methodology for identifying, assessing, mitigating, and monitoring these risks across an organization’s IT ecosystem. It transforms an ad-hoc response into a proactive, strategic function, aligning IT security with broader business objectives. This framework acts as a compass, guiding decision-makers through the intricate terrain of digital hazards and ensuring that technology investments are protected and yield their intended value.
What constitutes IT risk?
IT risk encompasses any potential threat that could negatively impact an organization’s information systems, data, or technology infrastructure. These risks can originate.
Why a structured approach is essential
A structured approach to IT risk management moves beyond isolated security measures to integrate risk considerations into every aspect of an organization’s operations. It fosters a culture of security awareness, ensuring that employees at all levels understand their role in protecting digital assets. Such a framework enables organizations to prioritize risks based on their potential impact and likelihood, allocating resources efficiently to address the most critical vulnerabilities first. This systematic methodology also facilitates better communication between IT departments and executive leadership, translating technical risks into business language that supports informed decision-making. By providing a clear roadmap, it helps avoid knee-jerk reactions to incidents and instead promotes a resilient, adaptive posture.
Key components of a robust risk management framework
An effective information technology risk management framework is built upon several foundational components that work in concert to provide comprehensive coverage. These components guide organizations through the entire risk lifecycle,, businesses can establish a strong defense against the ever-evolving threat landscape.
Risk identification and assessment
The initial phase involves meticulously identifying all potential IT risks within an organization’s environment. This includes reviewing hardware, software, network infrastructure, data processes, and human factors. Once identified, risks are assessed based on their likelihood of occurrence and their potential impact on business operations, financial standing, and reputation. This assessment often uses qualitative (e.g., high, medium, low) or quantitative (e.g., financial cost) methods to provide a clear understanding of the threat landscape. For example, assessing the likelihood of a data breach from a zero-day vulnerability might be high given the prevalence of such attacks, while the impact on customer trust and regulatory fines could be catastrophic. Tools like vulnerability scanners and penetration testing are crucial here.
Risk response and mitigation strategies
After risks are assessed, organizations must develop appropriate response and mitigation strategies. These strategies typically fall into four categories: avoidance, transference, acceptance, and mitigation. Avoidance involves eliminating the risk entirely, such as discontinuing a risky project. Transference shifts the risk to a third party, often through insurance. Acceptance means acknowledging the risk and deciding not to take any action, usually for low-impact, low-likelihood risks. Mitigation, the most common approach, involves implementing controls to reduce the likelihood or impact of the risk. This could include deploying firewalls, encrypting sensitive data, or implementing robust access controls. Each strategy requires careful consideration of cost, effectiveness, and alignment with business goals.
Continuous monitoring and review
The dynamic nature of technology and threats necessitates continuous monitoring and periodic review of the information technology risk management framework. This involves regularly scanning for new vulnerabilities, monitoring security events, and reviewing the effectiveness of existing controls. As new technologies are adopted or business processes change, new risks may emerge, requiring adjustments to the framework. Regular audits and assessments help identify gaps and ensure that the risk management process remains relevant and effective. Companies often use Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems to aggregate and analyze security logs, providing real-time insights into potential threats and compliance deviations. This ongoing vigilance is paramount for maintaining a strong security posture.
Implementing an effective information technology risk management framework
Implementing an effective information technology risk management framework is a complex undertaking that requires careful planning, executive buy-in, and a clear understanding of an organization’s specific context. It’s not a one-size-fits-all solution but rather a tailored process that aligns with the organization’s strategic objectives, regulatory requirements, and risk appetite. The success of implementation hinges on a phased approach, fostering collaboration across departments, and embedding risk awareness into the organizational culture. This strategic deployment ensures that the framework becomes an integral part of operations rather than an isolated security initiative.
Establishing governance and policies
The foundation of any successful risk management framework is strong governance. This involves establishing clear roles, responsibilities, and accountability for risk management activities across the organization. Senior leadership must champion the initiative, providing the necessary resources and demonstrating a commitment to security. Policies and procedures need to be developed that define acceptable use of technology, data handling protocols, incident response plans, and compliance requirements. These policies serve as the guiding principles for employees, ensuring a consistent approach to risk across all business units. Regular training and communication are essential to ensure that all stakeholders understand their obligations and the importance of these policies.
Integrating with business processes
For an information technology risk management framework to be truly effective, it cannot exist in a silo. It must be seamlessly integrated into existing business processes and workflows. This means considering risk implications during the planning stages of new projects, applications, and system deployments. Incorporating risk assessments into the software development lifecycle (SDLC) helps identify and address vulnerabilities early, reducing remediation costs later. Furthermore, integrating risk management with broader enterprise risk management (ERM) initiatives ensures a holistic view of risks across the entire organization, preventing IT risks.
Leveraging technology and automation
Modern IT risk management relies heavily on technology and automation to manage the sheer volume of data and rapidly evolving threats. Tools such as Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) platforms, vulnerability management systems, and security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR) solutions streamline processes, improve efficiency, and enhance accuracy. Automation can accelerate risk assessments, identify anomalies in real time, and even initiate predefined responses to security incidents. For instance, automated vulnerability scanning can continuously monitor systems for known weaknesses, while automated incident response playbooks can guide security teams through critical steps during an attack, reducing human error and response times. These technological enablers are crucial for maintaining an up-to-date and dynamic risk posture.
Benefits and business impact of strong IT risk management
Implementing a robust information technology risk management framework extends far beyond simply avoiding breaches or ensuring compliance; it fundamentally enhances an organization’s operational resilience and strategic agility. The benefits permeate various aspects of the business, fostering greater trust among customers and stakeholders, optimizing resource allocation, and even serving as a competitive differentiator in the marketplace. Companies that proactively manage their IT risks are better positioned to navigate unforeseen challenges and capitalize on new technological opportunities, ultimately driving long-term value.
Enhanced security posture and resilience
A well-implemented framework significantly strengthens an organization’s overall security posture. By systematically identifying and addressing vulnerabilities, companies can reduce their attack surface and minimize the likelihood of successful cyberattacks. In the event of an incident, a prepared organization with a defined incident response plan, a core component of risk management, can react swiftly and effectively, limiting damage and accelerating recovery. This enhanced resilience means less downtime, reduced data loss, and quicker restoration of normal operations, all of which directly impact profitability and customer satisfaction. It transforms a reactive defense into a proactive, adaptive system.
Regulatory compliance and reputation protection
In an era of stringent data privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA, and industry-specific mandates, demonstrating compliance is non-negotiable. An information technology risk management framework provides the documented processes and controls necessary to meet these regulatory obligations, avoiding hefty fines and legal repercussions. Beyond compliance, protecting sensitive data and maintaining operational integrity safeguards an organization’s reputation. Data breaches can severely erode customer trust and public perception, leading to long-term damage to brand equity. A strong risk management framework acts as a shield, preserving the trust that customers and partners place in the organization.
Improved decision-making and resource allocation
By providing clear insights into the organization’s risk landscape, an IT risk management framework empowers leadership to make more informed strategic and operational decisions. Resources, whether financial or human, can be allocated more effectively to address the most critical risks, ensuring maximum impact.
Evolving threats and the future of IT risk management
The pace of technological innovation is matched only by the increasing sophistication of cyber threats. New paradigms like artificial intelligence, quantum computing, and the widespread adoption of IoT devices are introducing novel risk vectors that traditional frameworks may not fully address. Therefore, the future of information technology risk management framework must be adaptive, forward-looking, and continuously integrate emerging technologies and methodologies to stay ahead of adversaries. Daily98news recognizes that staying abreast of these shifts is critical for any organization aiming for long-term digital security.
AI and machine learning in risk management
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are rapidly transforming the field of IT risk management. These technologies can process vast amounts of data to identify patterns, detect anomalies, and predict potential threats with unprecedented speed and accuracy. AI-powered tools can enhance threat detection, automate vulnerability assessments, and even assist in forensic analysis after an incident. For example, AI algorithms can analyze network traffic to spot unusual behavior indicative of an attack before it fully escalates, offering predictive capabilities that human analysts might miss. Organizations using AI-powered security systems can detect and contain data breaches significantly faster, leading to substantial cost savings. However, AI also introduces new risks, such as algorithmic bias or adversarial AI attacks, which must be managed within the framework itself.
The challenge of quantum computing and IoT security
The advent of quantum computing poses a long-term, yet significant, threat to current encryption standards, which form the bedrock of much of modern cybersecurity. Organizations need to start considering “post-quantum cryptography” readiness as part of their future risk strategies. Simultaneously, the proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices,, making them easy targets for attackers seeking to gain entry into corporate networks or launch large-scale distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks. Managing the security and risk associated with these myriad, often resource-constrained devices, is a growing challenge that demands specialized attention within the IT risk management framework.
The rise of supply chain and third-party risks
Modern businesses increasingly rely on a complex web of third-party vendors, cloud providers, and supply chain partners. This extended ecosystem, while enabling agility and specialization, also introduces significant inherent risks. A vulnerability in a single supplier’s system can have a cascading effect, compromising the data and operations of numerous clients, as evidenced by recent high-profile supply chain attacks. In fact, third-party vendor and supply chain compromise was the second most prevalent attack vector and second costliest in 2025. Therefore, an information technology risk management framework must extend its purview beyond the organization’s immediate perimeter to include thorough vetting, continuous monitoring, and contractual agreements with all third parties. AI-driven systems are increasingly being used to deliver end-to-end visibility across supply chain operations, proactively identifying risks associated with supplier delays, weather issues, and geopolitical disruptions. Robust due diligence and clear service level agreements regarding security are paramount to mitigate these pervasive external risks.
Conclusion
A well-defined and diligently executed information technology risk management framework is no longer a luxury but an an indispensable strategic asset in the contemporary digital economy. It provides the necessary structure and foresight to navigate an increasingly complex threat landscape, safeguarding critical assets, ensuring regulatory compliance, and bolstering an organization’s overall resilience. Daily98news encourages all technology leaders and business owners to invest in developing and continuously refining their IT risk management strategies, transforming potential vulnerabilities into areas of strength. By embracing a proactive and adaptive approach, organizations can build trust, protect their reputation, and confidently leverage technology to achieve their strategic objectives in an ever-evolving digital world.